POWERFUL
DISEASE CONTROL IN PsA2
RINVOQ met its ranked secondary endpoint of Minimal Disease Activity at Week 242
INDICATION
RINVOQ is indicated for the treatment of adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers.
Limitations of Use: RINVOQ is not recommended for use in combination with other Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine.
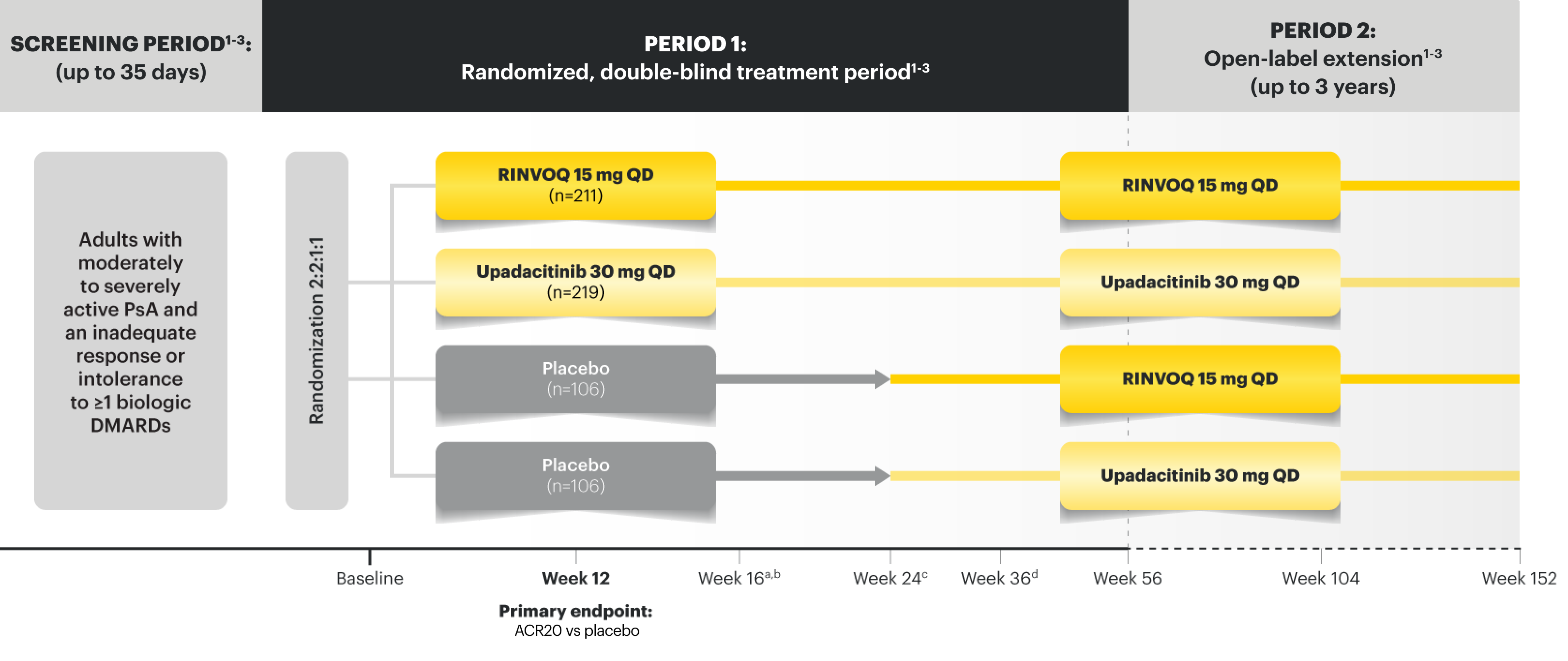
NRI Data From SELECT-PsA 2 (bDMARD-IR)1,2
RINVOQ 15 mg (n=211), Placebo (n=212)
ACR20 at Week 12
57%* RINVOQ vs 24% Placebo at Week 12
PRIMARY ENDPOINT
*P<0.001.2
SELECT-PsA 2 Study Design Intro
24‑week, double‑blind, placebo‑controlled study of 642 adult patients with moderately to severely active PsA who had an inadequate response or intolerance to at least 1 biologic DMARD. Patients were randomized to receive upadacitinib or placebo. The primary endpoint was proportion of patients achieving ACR20 response at Week 12 vs placebo.1
Please see Important Safety Information, including BOXED WARNING on Serious Infections, Mortality, Malignancies, Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events, and Thrombosis, below.
(n=53/211)
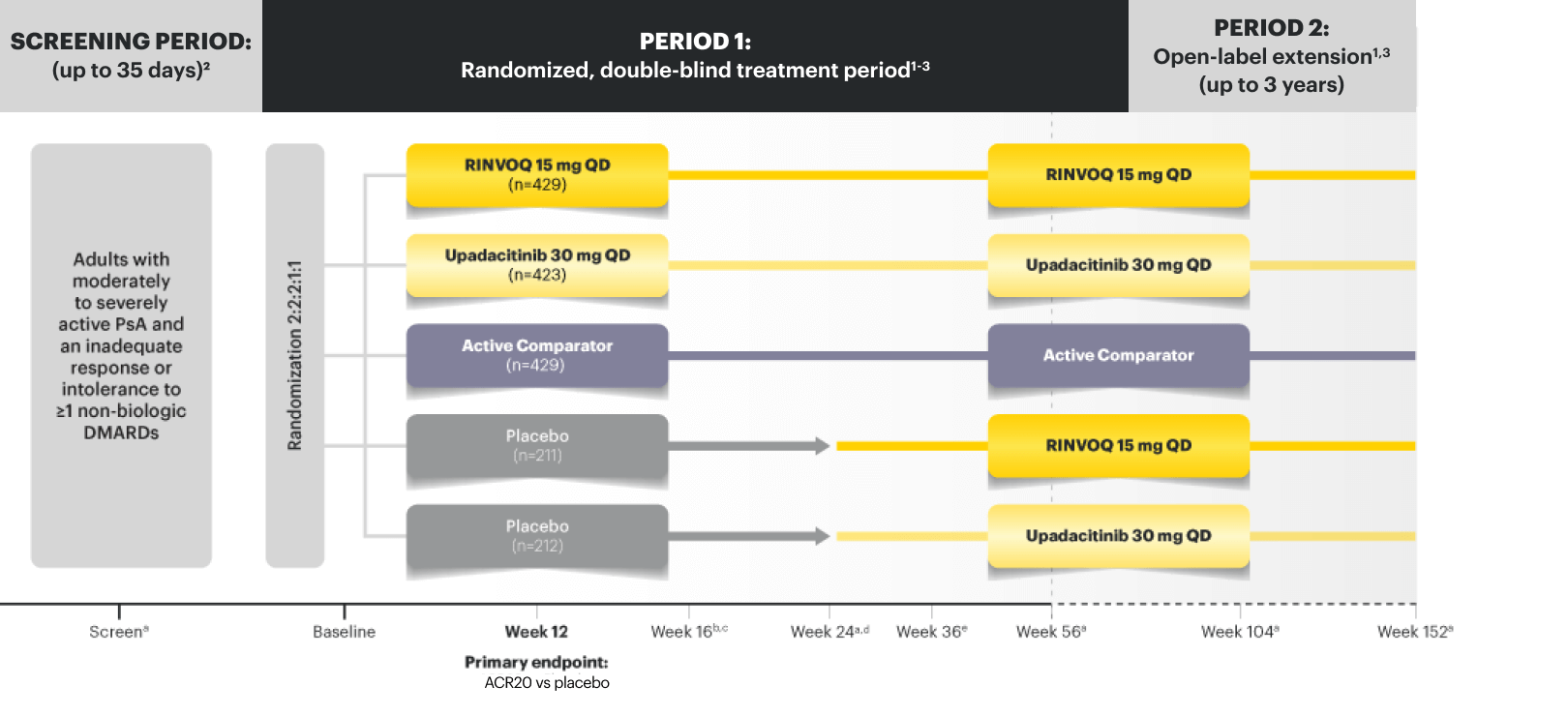
OF RINVOQ PATIENTS ACHIEVED MDA
vs 3% (n=6/212) placebo at Week 24 (Ranked Secondary Endpoint, NRI, P<0.001)2
Based on a post hoc analysis of SELECT-PsA 2 (NRI) of the 53 RINVOQ responders:2-4
72%
(n=38/53)
Met Tender Joint Count ≤1
81%
(n=43/53)
Met Swollen Joint Count ≤1
93%
(n=49/53)
Met PASI ≤1 or BSA-Psoriasis ≤3%†
60%
(n=32/53)
Met Pain ≤1.5 (0‑10 NRS)
83%
(n=44/53)
Met PtGA Disease Activity ≤2 (0‑10 NRS)
91%
(n=48/53)
Met HAQ-DI ≤1.5‡
100%
(n=53/53)
Met Leeds Enthesitis Index ≤1†
DATA LIMITATIONS: Post hoc subgroup analysis not included as a prespecified endpoint or controlled for multiplicity. The MDA responders’ placebo arm was insufficiently powered (n=6) to generate comparable subgroup data. Therefore, no conclusions can be drawn regarding the data.
†All patients regardless of presence of enthesitis or percent of BSA-Psoriasis at baseline were included in this evaluation.2
RINVOQ is not indicated for the treatment of plaque psoriasis1
44% of RINVOQ patients achieved MDA at ~3 years5
SELECT-PsA 2: bDMARD-IR Patients5
ALL DATA AS OBSERVED (AO)
In an As Observed (AO) analysis, patients with missing data at a specific time are not included, which may enrich the population and increase the response rates.
OLE LIMITATIONS: There is potential for enrichment of OLE data; unblinding patients may cause bias related to the overall treatment effect.
Safety Considerations
Serious Infections: RINVOQ-treated patients are at increased risk of serious bacterial (including tuberculosis [TB]), fungal, viral, and opportunistic infections leading to hospitalization or death. Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants, such as methotrexate or corticosteroids.
Mortality: A higher rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular (CV) death, was observed with a Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) in a study comparing another JAKi with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients ≥50 years with ≥1 CV risk factor.
Malignancies: Malignancies have occurred in RINVOQ-treated patients. A higher rate of lymphomas and lung cancer (in current or past smokers) was observed with another JAKi when compared with TNF blockers in RA patients.
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events: A higher rate of CV death, myocardial infarction, and stroke was observed with a JAKi in a study comparing another JAKi with TNF blockers in RA patients ≥50 years with ≥1 CV risk factor. History of smoking increases risk.
Thromboses: Deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and arterial thrombosis have occurred in patients treated for inflammatory conditions with JAK inhibitors, including RINVOQ. A higher rate of thrombosis was observed with another JAKi when compared with TNF blockers in RA patients.
Hypersensitivity: RINVOQ is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to RINVOQ or its excipients.
Other Serious Adverse Reactions: Hypersensitivity Reactions, Gastrointestinal Perforations, Laboratory Abnormalities, and Embryo-Fetal Toxicity.
Durable Joint Efficacy in PsA
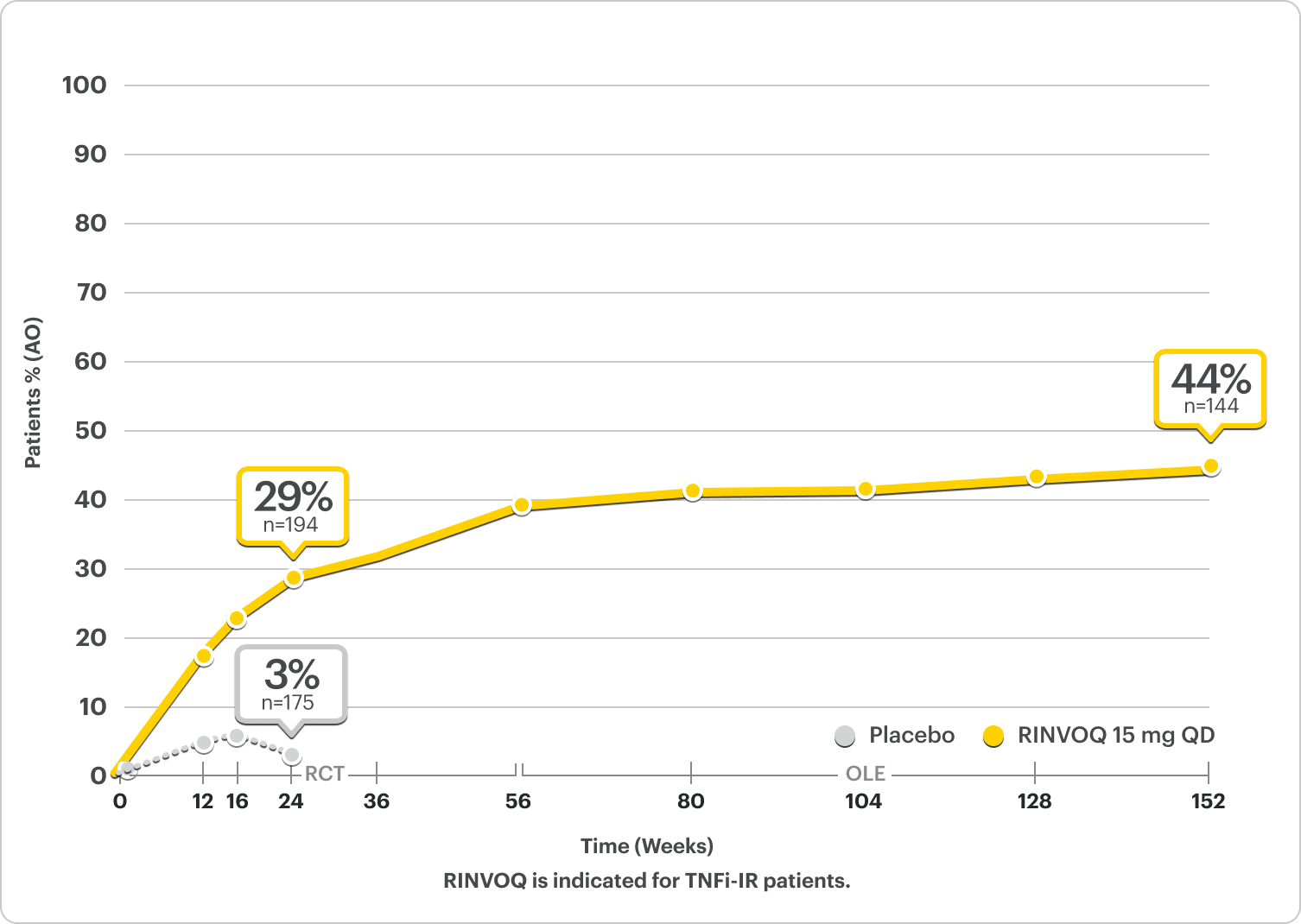
ACR20/50/70: Durable Joint Response Rates Out to 3 Years
NRI Data From SELECT-PsA 21,2
RINVOQ 15 mg (n=211), Placebo (n=212)
ACR20
33% RINVOQ vs 11% Placebo* at Week 2
57% RINVOQ vs 24% Placebo at Week 12
PRIMARY ENDPOINT
*P<0.001; analyses were not controlled for multiplicity; P-value obtained through nominal statistical testing.2
NRI Data From SELECT-PsA 22
RINVOQ 15 mg (n=211), Placebo (n=212)
ACR50
32%* RINVOQ vs 5% Placebo at Week 12
*P<0.001; analyses were not controlled for multiplicity; P-value obtained through nominal statistical testing.2
NRI Data From SELECT-PsA 22
RINVOQ 15 mg (n=211), Placebo (n=212)
ACR70
9%* RINVOQ vs 1% Placebo at Week 12
*P<0.001; analyses were not controlled for multiplicity; P-value obtained through nominal statistical testing.2
DATA LIMITATIONS2: Data labeled as a primary or ranked secondary endpoint were multiplicity controlled for comparisons. All other comparisons were not adjusted for multiplicity; therefore, statistical significance has not been established.
NRI Data From SELECT-PsA 24
RINVOQ (n=211), Placebo (n=212)
RAPID ACR20 RESPONSES
33% vs 11% placebo* at Week 2
57% vs 24% placebo at Week 12 PRIMARY ENDPOINT
ACR50
32% vs 5% placebo* at Week 12
ACR70
9% vs 1% placebo* at Week 12
*P<0.001; analyses were not controlled for multiplicity; P-value obtained through nominal statistical testing4
†P<0.0014
SELECT-PsA 2: bDMARD-IR Patients5
ALL DATA AS OBSERVED (AO)
In an As Observed (AO) analysis, patients with missing data at a specific time are not included, which may enrich the population and increase the response rates.
OLE LIMITATIONS: There is potential for enrichment of OLE data; unblinding patients may cause bias related to the overall treatment effect.
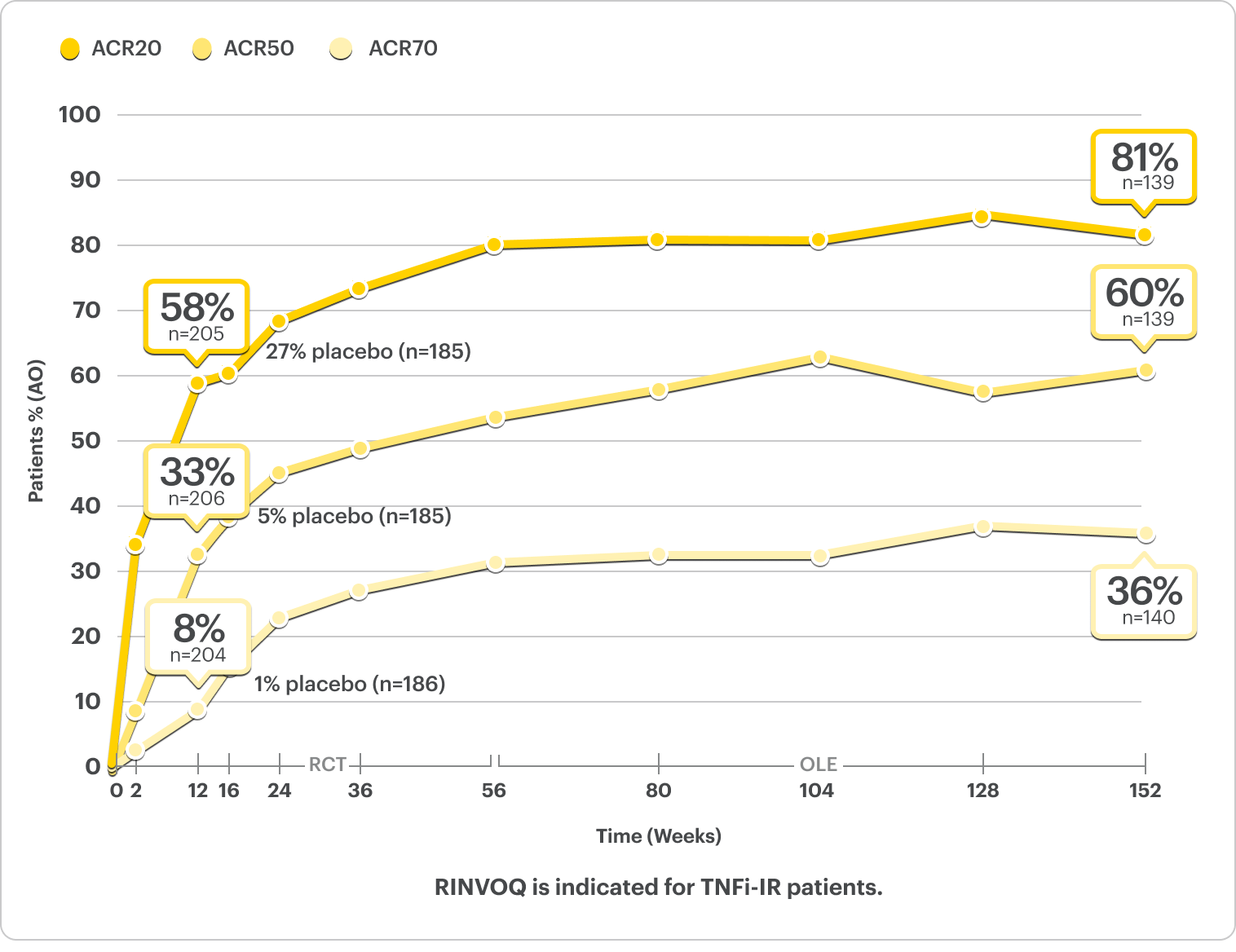
Complete Resolution of Enthesitis and Dactylitis Data6
NRI Data From SELECT-PsA 26
RINVOQ 15 mg (n=133), Placebo (n=144)
Enthesitis Resolution (LEI=0)†
43% RINVOQ vs 15% Placebo‡ at Week 24
†For subjects with baseline presence of enthesitis (LEI >0).
‡P≤0.05; analyses were not controlled for multiplicity; P-value obtained through nominal statistical testing.6
NRI Data From SELECT-PsA 26
RINVOQ 15 mg (n=55), Placebo (n=64)
Dactylitis Resolution (LDI=0)†
58% RINVOQ vs 28% Placebo‡ at Week 24
†For subjects with baseline presence of dactylitis (LDI >0).
‡P≤0.05; analyses were not controlled for multiplicity; P-value obtained through nominal statistical testing.6
DATA LIMITATIONS: Data labeled as a primary or ranked secondary endpoint were multiplicity controlled for comparisons. All other comparisons were not adjusted for multiplicity; therefore, statistical significance has not been established.2
Complete Resolution of Enthesitis (LEI=0)
SELECT-PsA 2: bDMARD-IR patients5
ALL DATA AS OBSERVED (AO)
For subjects with baseline presence of enthesitis (LEI >0).
In an As Observed (AO) analysis, patients with missing data at a specific time are not included, which may enrich the population and increase the response rates.
OLE LIMITATIONS: There is potential for enrichment of OLE data; unblinding patients may cause bias related to the overall treatment effect.
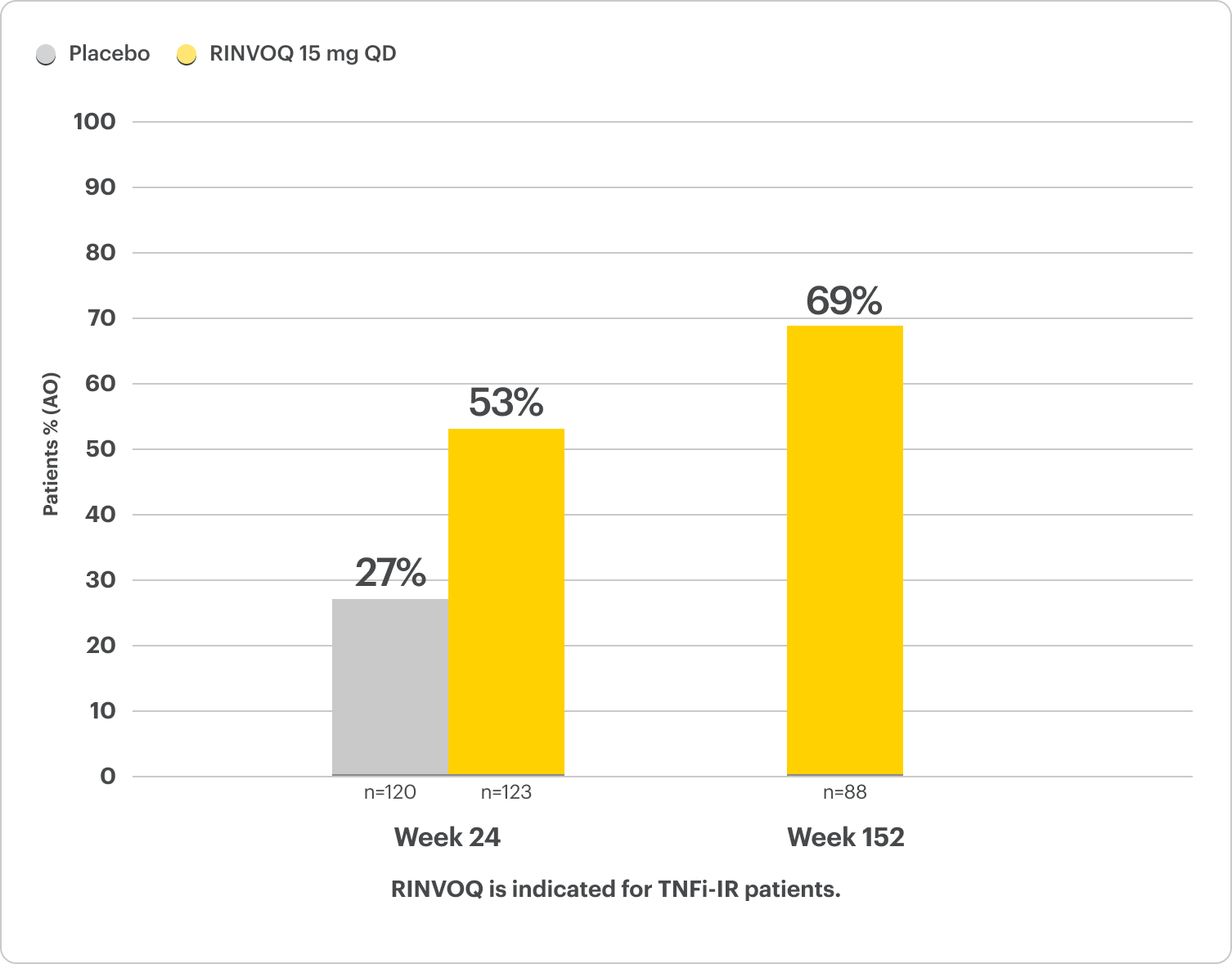
Complete Resolution of Dactylitis (LDI=0)
SELECT-PsA 2: bDMARD-IR patients5
ALL DATA AS OBSERVED (AO)

For subjects with baseline presence of enthesitis (LEI >0).
In an As Observed (AO) analysis, patients with missing data at a specific time are not included, which may enrich the population and increase the response rates.
OLE LIMITATIONS: There is potential for enrichment of OLE data; unblinding patients may cause bias related to the overall treatment effect.
Durable HAQ-DI responses for RINVOQ up to ~3 years7
SELECT-PsA 2: bDMARD-IR patients
ALL DATA AS OBSERVED (AO)
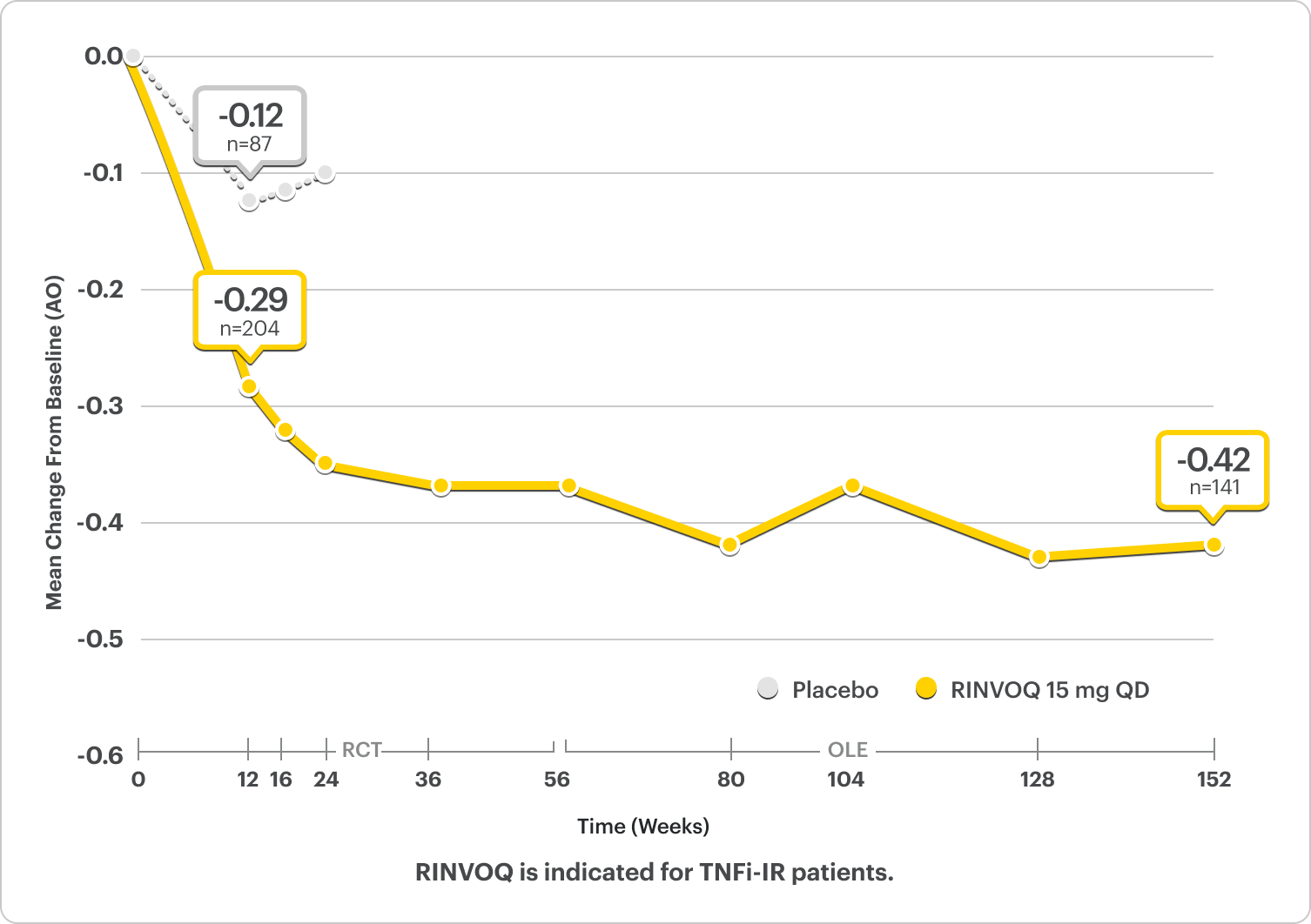
*P<0.001 for RINVOQ vs placebo.2
Improvement in Physical Function2,5
LS Mean ∆HAQ-DI From Baseline at Week 12 was -0.30* for RINVOQ (n=199) vs -0.10 for Placebo (n=180) (MMRM) (Ranked Secondary Endpoint)2
In an As Observed (AO) analysis, patients with missing data at a specific time are not included, which may enrich the population and increase the response rates.
OLE LIMITATIONS: There is potential for enrichment of OLE data; unblinding patients may cause bias related to the overall treatment effect.
Please see Important Safety Information, including BOXED WARNING on Serious Infections, Mortality, Malignancies, Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events, and Thrombosis, below.
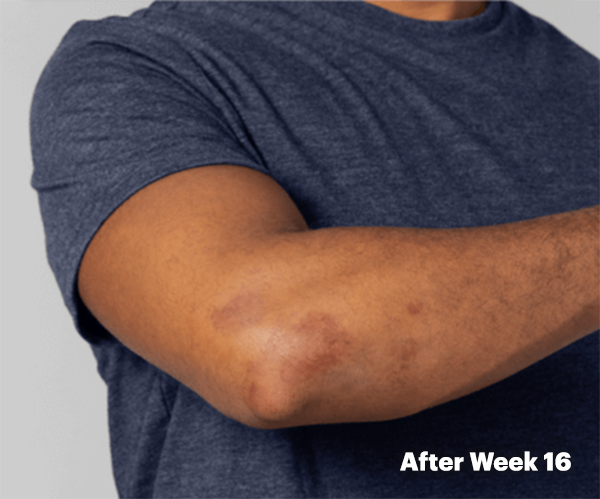
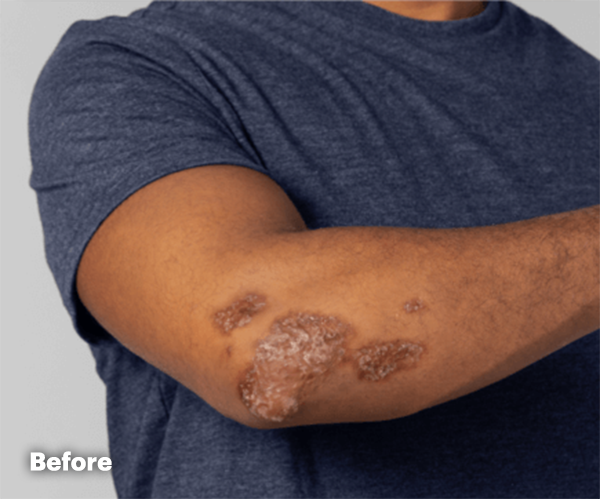
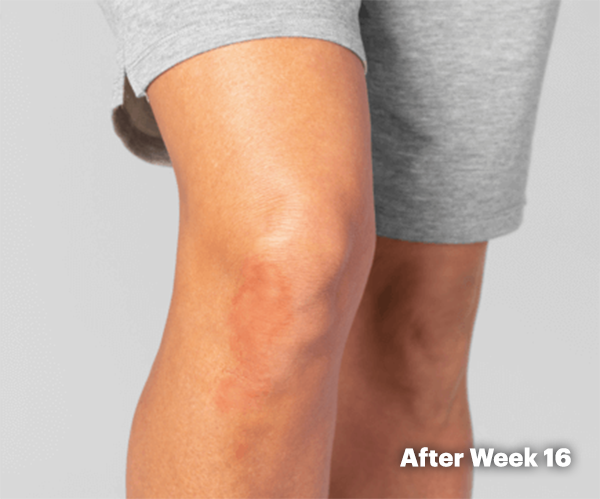
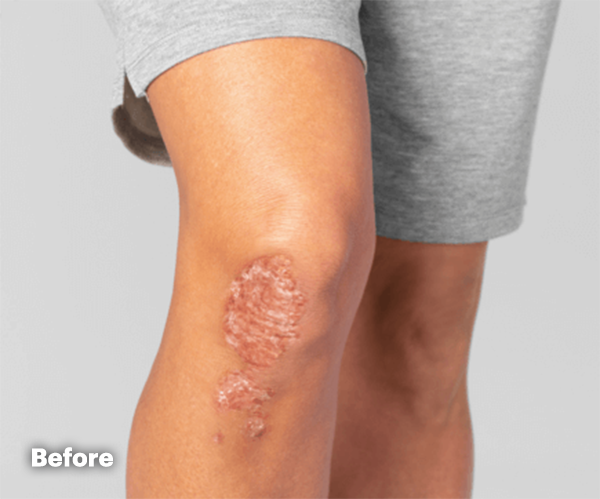
PsA Skin Clearance Before and After
In SELECT-PsA 2, 52% of RINVOQ Patients Achieved PASI 75 at Week 16 (Ranked Secondary Endpoint, NRI, P<0.001) vs 16% Placebo2
Drag the slider below to see results.
Illustration of PASI assessed in patient with psoriatic skin involvement ≥3% BSA at baseline
Illustration of PASI assessed in patient with psoriatic skin involvement ≥3% BSA at baseline
RINVOQ has not been studied in and is not indicated for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.1
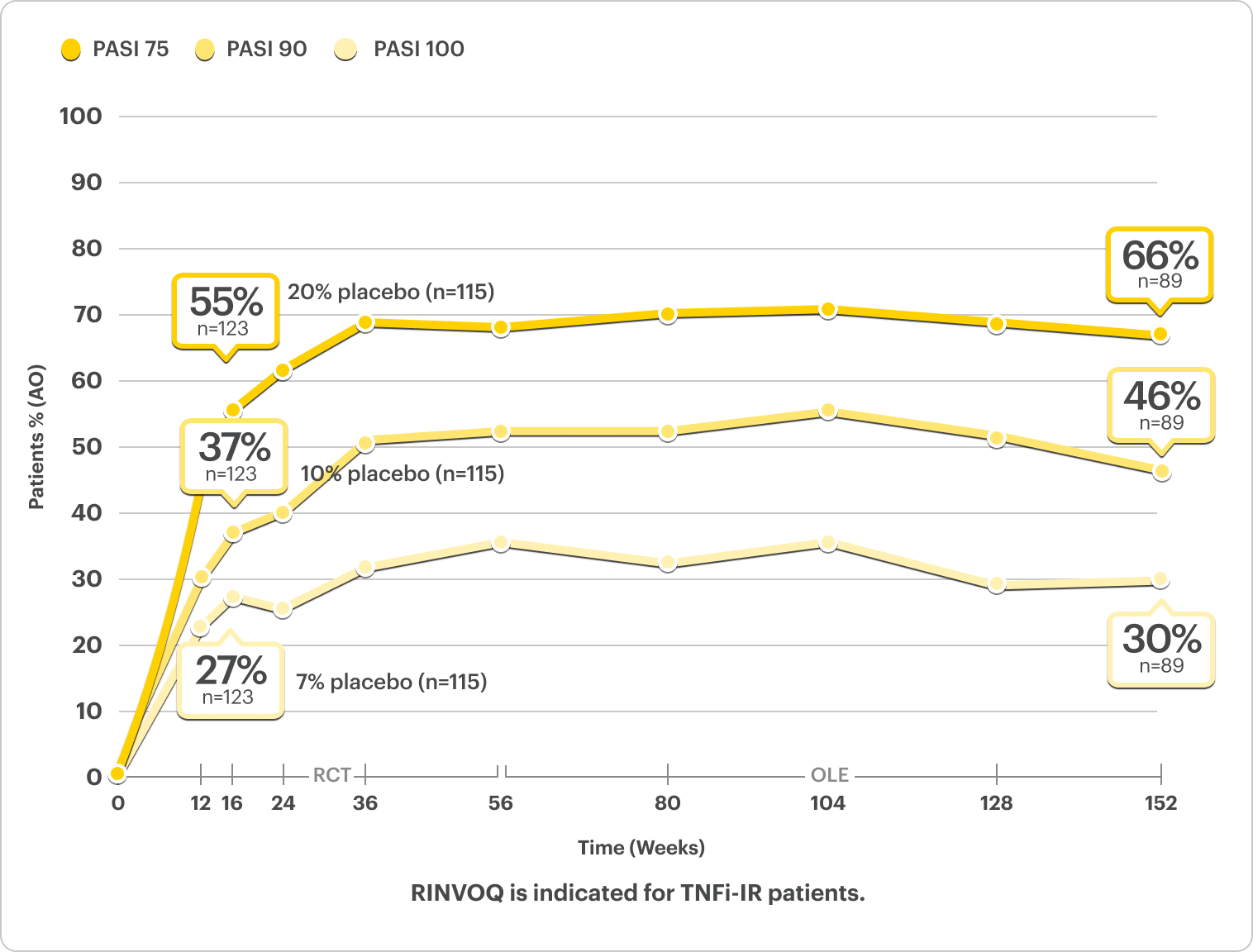
Skin Clearance Data
PASI Response Rates Through ~3 Years5*†
NRI Data from SELECT-PsA 22
RINVOQ 15 mg (n=130), Placebo (n=131)
PASI 75†
52%* RINVOQ vs 16% Placebo at Week 16
RANKED SECONDARY ENDPOINT
PASI 90†
35%* RINVOQ vs 8% Placebo at Week 16
PASI 100†
25%* RINVOQ vs 6% Placebo at Week 16
*P<0.001.2
†PASI assessed in patients with psoriatic skin involvement of ≥3% BSA at baseline.2
RINVOQ is not indicated for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.1
DATA LIMITATIONS: Data labeled as a primary or ranked secondary endpoint were multiplicity controlled for comparisons. All other comparisons were not adjusted for multiplicity; therefore, statistical significance has not been established.
NRI Data From SELECT-PsA 24
RINVOQ (n=211), Placebo (n=212)
RAPID ACR20 RESPONSES
33% vs 11% placebo* at Week 2
57% vs 24% placebo at Week 12 PRIMARY ENDPOINT
ACR50
32% vs 5% placebo* at Week 12
ACR70
9% vs 1% placebo* at Week 12
*P<0.0012
†PASI assessed in patients with psoriatic skin involvement of ≥3% BSA at baseline2,4

Interested in the safety data for RINVOQ?
See RINVOQ’s safety data across clinical trials

Explore RINVOQ data in gastroenterology
For moderate to severe Crohn's disease (CD) or moderate to severe ulcerative colitis (UC) in adult TNFi-IR patients1